Mycological resource management in Ethiopia
Production of Morchella sp.
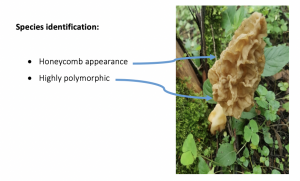
Habitat:
Adapted to a wide range of habitats and environmental conditions.
- Some species fruit in non-disturbed forests in association with living trees.
- Others fruit in great abundance with trees that are declining, dying, or recently dead
Management guidelines:
Fruiting triggered by light stand disturbances
- stand thinning,
- selective logging
- controlled burns
For intense management, the production of morels can be reinforced with the introduction of mycelium in the soil in suitable stands.
This requires previous studies about which species occur naturally and strain isolation and spawn production in microbiology laboratories.
Finally, it can be also grown in greenhouses following the same procedure: introduction of large amounts of mycelium in the soil, colonization and expansion phase and induction of fructification.
Mycological resource management in Ethiopia
Production of Suillus luteus

Habitat:
Non-native Pinus plantations.
Ecology:
- Suillus luteusis a pioneer species that typically establishes in the early stages of forest succession.
- The fungus forms mycorrhizal associations with various pine species
Management guidelines:
- Because of its pioneering ecology, it is necessary to maintain the young stands, favoring the rejuvenation of the pine plantations.
- Due to the moderately heliophilic character, it will be interesting to open clearings in the plantations that allow light to enter.
- It would be interesting to study the possibility to favor an evolution of stands towards to the production of Boletus edulis, a species that is more economically valued. There are previous experiences of introducing Boletus outside its natural range of distribution.
Use:
- Cooked before eating.
- Some authors recommend to dicard the glutinous cuticle and tubes before cooking.